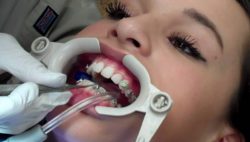
What is Enamel Hypoplasia?
Enamel Hypoplasia can be a lifelong condition that patients continue to treat or a major problem that requires fillings, crowns, and even tooth extractions. To understand the cause of enamel deficiencies and how to treat and prevent them, you need to know how your enamel works and why it doesn’t always form correctly. Keep reading to learn more about Enamel Hypoplasia and how dentists treat it.
Enamel is the hard, protective covering on the outside of your teeth. It is the hardest part of your body and works like a suit of armor protecting the soft and sensitive areas. It’s because of enamel that you’re able to eat a bowl of hot soup or enjoy ice cream in the middle of summer without your teeth experiencing pain. This protective coating also fights against physical attacks on the teeth, like biting down on hard candy and ice cubes.
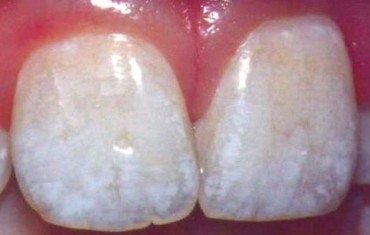
Unfortunately, tooth enamel is almost 90% mineral, which dissolves in acidic environments like our mouths. When we eat highly acidic foods like fruit or candy — not to mention soda — the bacteria in our mouths turn it into lactic acid, which can wear away enamel. Once your protective layer of enamel is gone, if can’t grow back, which is why so many dentists emphasize good oral hygiene from a young age to keep the suit of armor strong.
However, kids and adults don’t always end up with the right amount of enamel on their teeth, and can suffer from Enamel Hypoplasia. This article will focus primarily on its causes, effects, and treatment.

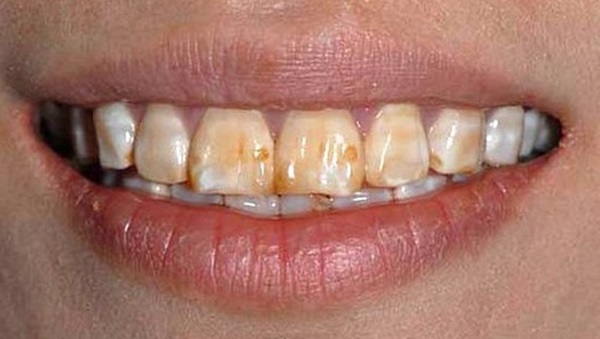
Hypoplasia is an enamel deficiency that leaves the teeth vulnerable to damage and decay. It often takes the form of grooves, pits, or lines within teeth, either across the surface or in certain spots. Depending on the severity, Enamel Hypoplasia can look like a small dent in the tooth, or take up several teeth throughout the mouth. There can be localized discoloration, or the entire tooth can turn a dark brown color. This can make the mouth incredibly sensitive, especially for toddlers that are just learning to communicate how they feel.
While Enamel Hypoplasia can occur in both baby and adult teeth, it’s often developed before the age of three. As the baby teeth are growing, the enamel is still soft and weak, creating opportunities for damage early on. Two types of causes are attributed to Enamel Hypoplasia: hereditary and environmental.
One of the most important factors in treating Enamel Hypoplasia is catching it early. It’s better for the dentist to spot a sensitive area or fill a small cavity early on than to remove the whole tooth due to extensive decay.
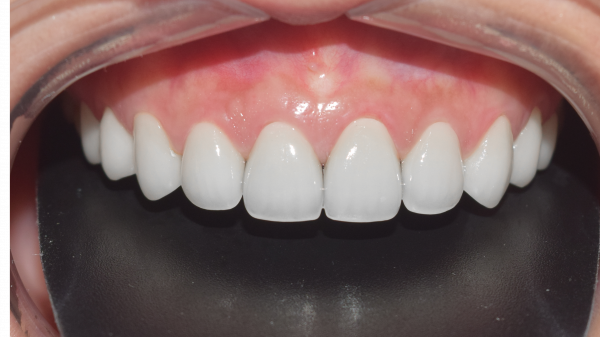
Veneer as one of the methods to fix enamel hypoplasia
- Published in General Dentistry, Tin tức
NIỀNG RĂNG MẤT BAO LÂU? – NIỀNG RĂNG UY TÍN TẠI NHA KHOA DND
Không thể phủ nhận các lợi ích tuyệt vời sau khi niềng răng đem lại cho chúng ta, không chỉ vấn đề thẩm mỹ tăng lên mà còn giảm thiểu các bệnh lý về răng miệng. Hiện nay, niềng răng vẫn là phương pháp tốt nhất giúp bạn sở hữu nụ cười với những chiếc răng đều như chia. Đặc biệt, với sự hỗ trợ đắc lực của các công nghệ hiện đại, niềng răng không mất thời gian như bạn vẫn nghĩ.
Niềng răng là gì và khi nào cần niềng răng?
Niềng răng – chỉnh nha là phương pháp sử dụng các khí cụ nha khoa nhằm sắp xếp, di chuyển các răng và khớp cắn về đúng vị trí mong muốn nhằm đem lại nụ cười thẩm mỹ nhất cho khuôn mặt.

Tất cả mọi người gặp phải các trường hợp về răng và khớp cắn dưới đây thì đều nên niềng răng:
- Răng lệch lạc, khấp khểnh, chen chúc,…
- Răng thưa
- Răng gặp các vấn đề về khớp cắn: hô, vẩu, khớp cắn đối đầu, cắn chìa,…
Niềng răng có lâu không?
Phụ thuộc vào nhiều yếu tố, tình trạng răng miệng khác nhau ở mỗi người và kế hoạch điều trị của các bác sĩ chỉnh nha mà thời gian niềng răng cũng diễn ra dài hay ngắn. Sau khoảng thời gian trung bình từ 15 tháng đến 24 tháng, các vấn đề về răng của bạn sẽ hoàn toàn biến mất nhờ niềng răng, thay vào đó là một nụ cười đẹp với những chiếc răng đều và khớp cắn chuẩn.
Niềng răng là một quá trình dài, bền bỉ đối với bản thân khách hàng và người nha sĩ, trong đó sự quyết tâm, kiên trì của bệnh nhân là vô cùng quan trọng và chiếm tới 50% thành công của một ca niềng răng. Mọi sự dịch chuyển đều có tính toán nhằm đem đến giá trị tốt nhất cho bạn nên quá trình tịnh tiến răng cần từ từ, đều đặn và liên tục. Vì vậy, niềng răng không quá lâu như bạn vẫn nghĩ, bạn cần tin tưởng bác sĩ điều trị cho mình và tuân thủ theo những chỉ định mà bác sĩ đưa ra.
Quy trình niềng răng tại Nha khoa DND như thế nào?
Tùy từng trường hợp răng khác nhau, kế hoạch điều trị khác nhau của mỗi bác sĩ mà một quy trình niềng răng cũng khác nhau. Dưới đây là một quy trình niểng răng đơn giản, sử dụng mắc cài kim loại (hoặc sứ) tiêu chuẩn, không cần sự hỗ trợ của các khí cụ chỉnh nha hỗ trợ (cắm vis), không phải nhổ răng (răng thừa, nhổ R4 tạo khoảng).
- Bước 1: Thăm khám tổng quát, chụp ảnh, lấy dấu nghiên cứu
Đây là bước đầu tiên khi bạn bắt đầu quan tâm tới việc niềng răng. Các bác sĩ sẽ thực hiện các bước thăm khám tổng quát, chụp phim X-quang 2D, 3D nhằm đánh giá tình trạng răng ban đầu của bạn, phần xương hàm, cung hàm, từ đó các bác sĩ sẽ đưa ra kế hoạch điều tri phù hợp.
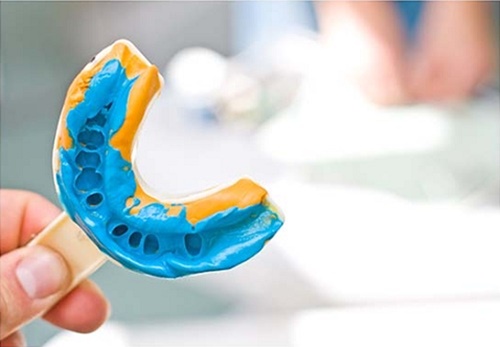
Lấy dấu răng trong chỉnh nha
Sau đó các bác sĩ sẽ chụp ảnh trong miệng, ngoài mặt và lấy dấu răng để làm tư liệu nghiên cứu. Sau khoảng từ 1 – 3 ngày, bác sĩ sẽ gửi kế hoạch điều trị chi tiết đến bạn.
- Bước 2: Gắn mắc cài
Nếu bạn đồng ý với kế hoạch điều trị bác sĩ đưa ra, bạn sẽ bắt đầu quá trình chỉnh nha ngay sau đó. Các bước bao gồm:
- Làm sạch răng: lấy cao răng và đánh bóng
- Gắn mắc cài: Đo đạc và xác định vị trí gắn mắc cài, cố định bằng composite chuyên dụng trong nha khoa để composite để mắc cài bám trụ vững chắc trên bề mặt răng.
- Cố định dây cung vào các rãnh mắc cài bằng thun buộc
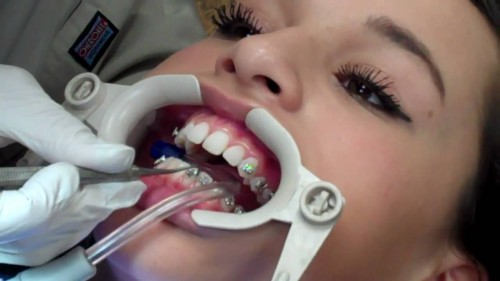
Gắn mắc cài
- Bước 3: Tái khám định kỳ
Định kỳ thời gian từ 4 – 6 tuần, bạn sẽ tái khám để kiểm tra tiến độ tịnh tiến của răng, thay chun, tăng lực tác động và thực hiện các bước tiếp theo của kế hoạch điều trị chi tiết ban đầu. Sau mỗi lần tái khám, có thể răng bạn sẽ hơi đau nhức một chút do lực thay đổi và nhanh chóng biến mất sau khoảng 1 – 2 ngày.
Khoảng thời gian trung bình từ 15 – 24 tháng, khi răng bạn đã đều và đẹp, khớp cắn đã về đúng chuẩn cũng là lúc quá trình niềng răng kết thúc. Bạn sẽ sở hữu nụ cười thẩm mỹ hơn và chức năng của răng cũng được cải thiện.
- Published in Chưa được phân loại
What is a dental filling?
What is a dental filling?
A dental filling is a way to restore a tooth damaged by decay back to its normal function and shape. When a dentist gives you a filling, he or she first removes the decayed tooth material, cleans the affected area, and then fills the cleaned out cavity with a filling material.
By closing off spaces where bacteria can enter, a filling also helps prevent further decay. Materials used for fillings include gold, porcelain, a composite resin (tooth-colored fillings), and an amalgam (an alloy of mercury, silver, copper, tin and sometimes zinc).
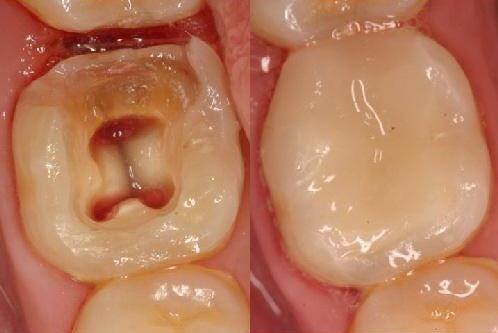
Dental filling for tooth decay
Which Type of Filling is Best?
No one type of filling is best for everyone. What’s right for you will be determined by the extent of the repair, whether you have allergies to certain materials, where in your mouth the filling is needed, and the cost. Considerations for different materials include:
- Gold fillings are made to order in a laboratory and then cemented into place. Gold inlays are well tolerated by gum tissues, and may last more than 20 years. For these reasons, many authorities consider gold the best filling material. However, it is often the most expensive choice and requires multiple visits.
- Amalgam (silver) fillings are resistant to wear and relatively inexpensive. However, due to their dark color, they are more noticeable than porcelain or composite restorations and are not usually used in very visible areas, such as front teeth.
- Composite (plastic) resins are matched to be the same color as your teeth and therefore used where a natural appearance is desired. The ingredients are mixed and placed directly into the cavity, where they harden. Composites may not be the ideal material for large fillings as they may chip or wear over time. They can also become stained from coffee, tea or tobacco, and do not last as long as other types of fillings generally from three to 10 years.
- Porcelain fillings are called inlays or onlays and are produced to order in a lab and then bonded to the tooth. They can be matched to the color of the tooth and resist staining. A porcelain restoration generally covers most of the tooth. Their cost is similar to gold.
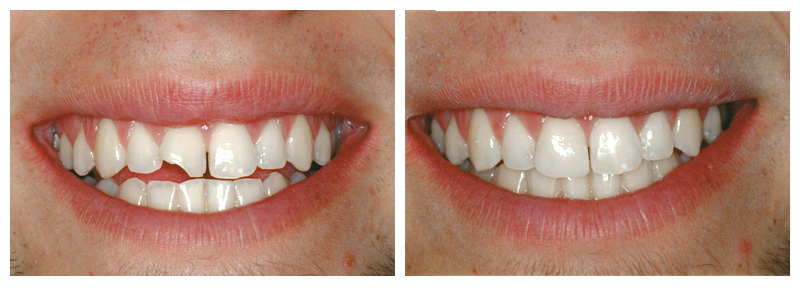
If decay or a fracture has damaged a large portion of the tooth, a crown, or cap, may be recommended. Decay that has reached the nerve may be treated in two ways: through root canal therapy (in which nerve damaged nerve is removed) or through a procedure called pulp capping (which attempts to keep the nerve alive).
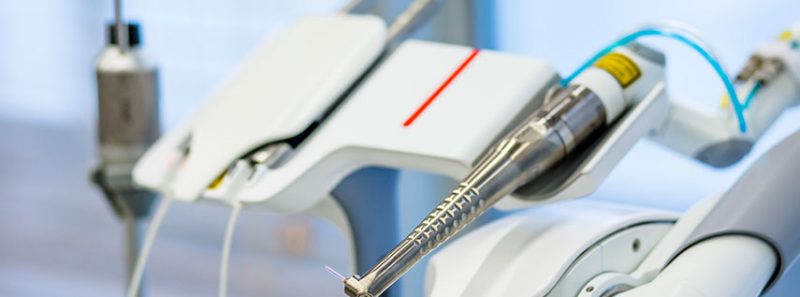
Laser Lightwalker technology
What Happens When You get a Filling?
If your dentist decides to fill a cavity, he or she will first remove the decay and clean the affected area. The cleaned-out cavity will then be filled with any of the variety of materials described above.
How Do I Know if I Need a Filling?
Only your dentist can detect whether you have a cavity that needs to be filled. During a checkup, your dentist will use a small mirror to examine the surfaces of each tooth.
Anything that looks abnormal will then be closely checked with special instruments. Your dentist may also X-ray your entire mouth or a section of it. The type of treatment your dentist chooses will depend on the extent of damage caused by decay.
- Published in Dental Care, Tin tức
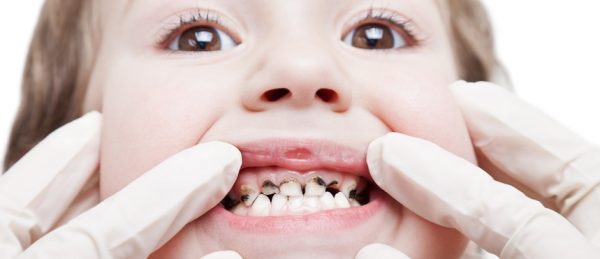
Tooth decay prevention
Tooth decay is the destruction of tooth structure and can affect both the enamel (the outer coating of the tooth) and the dentin layer of the tooth.
Tooth decay occurs when foods containing carbohydrates (sugars and starches), such as breads, cereals, milk, soda, fruits, cakes, or candy are left on the teeth. Bacteria that live in the mouth digest these foods, turning them into acids. The bacteria, acid, food debris, and saliva combine to form plaque, which clings to the teeth. The acids in plaque dissolve the enamel surface of the teeth, creating holes in the teeth called cavities.
To prevent tooth decay:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a fluoride-containing toothpaste. Preferably, brush after each meal and especially before going to bed.
- Clean between your teeth daily with dental floss or interdental cleaners, such as the Oral-B Interdental Brush, Reach Stim-U-Dent, or Sulcabrush.
- Rinse daily with a fluoride-containing mouthwash. Some rinses also have antiseptic ingredients to help kill bacteria that cause plaque.
- Eat nutritious and balanced meals and limit snacks. Avoid carbohydrates such as candy, pretzels and chips, which can remain on the tooth surface. If sticky foods are eaten, brush your teeth soon afterwards.
- Check with your dentist about use of supplemental fluoride, which strengthens your teeth.
- Ask your dentist about dental sealants (a plastic protective coating) applied to the chewing surfaces of your back teeth (molars) to protect them from decay.
- Drink fluoridated water. At least a pint of fluoridated water each day is needed to protect children from tooth decay.
- Visit your dentist regularly for professional cleanings and oral exam.

Researchers are developing new means to prevent tooth decay. One study found that a chewing gum that contains the sweetener xylitol temporarily retarded the growth of bacteria that cause tooth decay. In addition, several materials that slowly release fluoride over time, which will help prevent further decay, are being explored. These materials would be placed between teeth or in pits and fissures of teeth. Toothpastes and mouth rinses that can reverse and “heal” early cavities are also being studied.
- Published in General Dentistry, Tin tức